

|
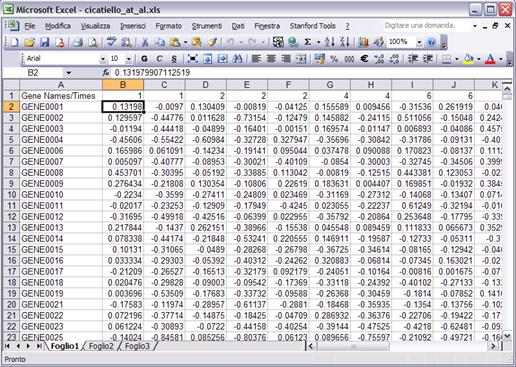
The data file should be contained in a .xls or .txt tab delimited file prepared as follows:
The first row should contain in the first column a text string and in the remaining columns the numeric values of the time variable, for all the samples in the same unit (either seconds, hours, days, etc.), with the samples ordered in ascending order. The first column (from the second row on) should contain gene identifiers: identifiers are unique strings (characters or combinations of characters and numbers). The remaining cells will contain the data in the form of log-scale signal to reference ratios. Data have to be already normalized. Missing values can be denoted either by empty cell or with NaN
|
|
A user friendly software for Bayesian Analysis of Time Series Microarray Experiments. |


|
Bayesian Analysis for Time Series Microarray Experiments |

|
Gene Name or Gene Id |

|
Data (normalized in log2 scale) and with empty cell or NaN for missing values |


